Soil Management
Soil is the living engine of agriculture. Healthy soil supports crops, conserves water, prevents erosion, and boosts long-term farm productivity. In organic farming, soil management is not just a routine practice—it is the core philosophy. A farmer who understands soil properly can reduce input costs, improve crop yields, and build a resilient farm ecosystem.
This detailed guide covers everything you need to know about soil health, soil improvement methods, testing, organic amendments, and long-term farm planning.
🌾 1. What Is Soil Management?
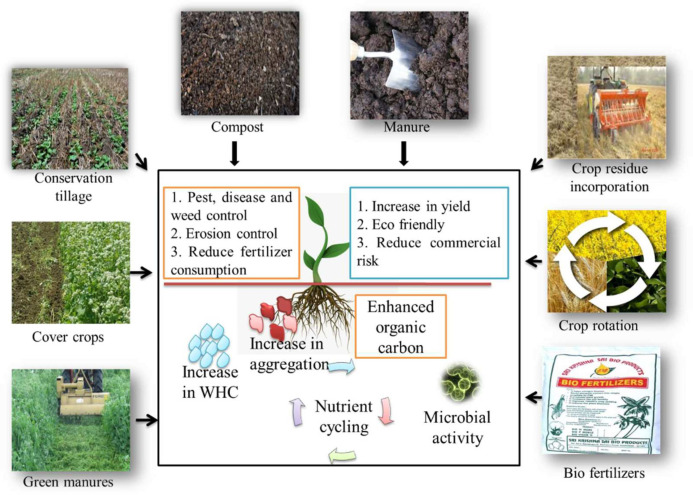
Soil management refers to all the practices used to maintain, improve, and protect the soil’s physical, chemical, and biological properties. Good soil management ensures:
✓ Proper nutrient availability
✓ Better root development
✓ Increased water retention
✓ Reduced erosion
✓ Higher organic matter content
In organic farming, the goal is to work with nature, not against it—focusing on soil regeneration instead of heavy synthetic inputs.
🌍 2. Why Soil Health Matters in Organic Farming
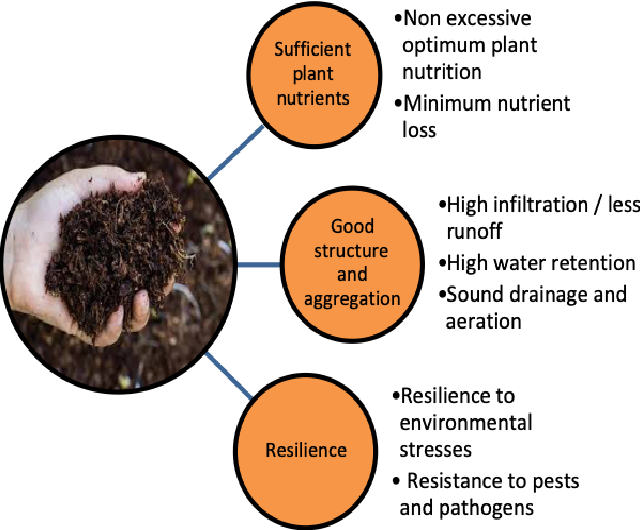
Healthy soil behaves like a balanced ecosystem. It contains billions of microorganisms, beneficial fungi, earthworms, and organic matter—all working together.
🌟 Key Benefits:
- 🌱 Natural fertility without synthetic fertilizers
- 💧 Better water-holding capacity
- 🐛 Reduced pest and disease pressure (healthy soil = healthy plants)
- 🍃 Improved nutrient cycling
- 🌾 Stable yields in long term
Studies show that soil organic matter is the strongest indicator of farm productivity, especially in climate-variable regions.
🔬 3. Soil Testing: The First Step of Smart Farming
Before applying any fertilizer or amendment, farmers must understand what the soil already contains.
✔️ Types of Soil Testing:
- pH Test: Determines acidity/alkalinity
- NPK Test: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium levels
- Micronutrient Test: Zinc, Iron, Boron, Magnesium, Sulphur
- Organic Carbon Test: Indicates soil health
- EC Test: Measures salinity
📌 When to Test?
- Before sowing
- After harvest
- Every 6–12 months
📌 Ideal Soil pH:
Most crops prefer 6.0–7.5 for optimum nutrient absorption.
🍂 4. Improving Soil Structure Naturally
Soil structure affects water flow, aeration, root penetration, and microbial activity.
🌱 Methods to Improve Soil Structure:
1. Add Organic Matter
- Compost
- Farmyard manure (FYM)
- Vermicompost
- Green manure crops
Organic matter increases porosity and encourages microbial life.
2. Mulching
Using straw, dry leaves, crop residues:
✓ Reduces evaporation
✓ Prevents weed growth
✓ Protects soil organisms
3. Crop Rotation
Alternate crops such as:
- Legumes → Rice → Vegetables
- Millets → Pulses → Oilseeds
Rotation helps break disease cycles and improves soil balance.
🌱 5. Microbial Life: The Hidden Workforce of Soil
Organic soil management revolves around supporting beneficial microbes. These unseen organisms:
- Fix atmospheric nitrogen
- Decompose organic matter
- Release nutrients in plant-available form
- Suppress harmful pathogens
🔥 Popular Organic Inputs to Boost Microbial Activity:
- Jeevamrutham / Jeevamrut
- Panchagavya
- Fish Amino Acid (FFA)
- Banana Pseudostem Extract
- Vermiwash
These solutions act as natural bio-boosters.
🌧️ 6. Soil Moisture Management
Water availability influences nutrient uptake. Organic practices improve moisture efficiency.
Best Techniques:
- Drip irrigation
- Mulching
- Contour trenches in sloped fields
- Raised beds for vegetables
- Organic matter addition
Organic soils hold 20–30% more moisture than conventionally managed soils.
🌾 7. Preventing Soil Erosion
Erosion leads to loss of topsoil and nutrients.
Effective Control Measures:
- Contour plowing
- Cover crops (cowpea, sunhemp, dhaincha)
- Windbreaks
- Mulching on bare soil
- Terracing in hill regions
Even a 1 cm loss of topsoil can reduce yields significantly.
🧪 8. Nutrient Management in Organic Farming
Instead of chemical fertilizers, organic nutrient sources feed the soil slowly and steadily.
Natural Nutrient Sources:
- Nitrogen: Compost, neem cake, legume cover crops
- Phosphorus: Rock phosphate, bone meal
- Potassium: Wood ash, banana stem extract
- Micronutrients: Seaweed, panchagavya, ferrous sulphate (limited use)
✔️ Fertigation via Drip:
Liquid organic fertilizers like fish amino, humic acid, and cow-urine solutions are used for uniform application through drip systems.
🌱 9. Cover Crops & Green Manures
Cover crops prevent soil exposure and add biomass.
Examples:
- Sunhemp
- Cowpea
- Greengram
- Sesbania (Dhaincha)
They fix nitrogen and improve soil texture.
🛠️ 10. Long-Term Soil Regeneration Strategies
To build soil that lasts generations:
- Maintain 3–5% organic carbon
- Avoid excessive tilling
- Reduce chemical inputs
- Encourage biodiversity
- Add compost yearly
- Use livestock integration for manure
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the best way to improve soil health naturally?
Adding organic matter (compost, FYM, green manure) is the fastest and safest method.
2. How often should soil be tested?
Ideally once every year or at least before major cropping seasons.
3. What pH level is ideal for farming?
Most crops grow best between 6.0 and 7.5.
4. Are chemical fertilizers harmful to soil?
Excessive chemical use can reduce microbial life, increase acidity, and weaken soil over time.
5. Which crops improve soil fertility?
Legumes like sunhemp, cowpea, greengram, and dhaincha help fix nitrogen naturally.
6. Does organic farming increase yield?
In the long term, organic farming stabilizes yields, improves soil quality, and reduces input cost.
🌱 Conclusion
Soil management is the true backbone of sustainable and organic farming. A farmer who nurtures the soil nurtures the future. By increasing organic matter, protecting microbes, managing water wisely, and reducing chemicals, farmers can achieve healthier crops, better income, and ecological balance.
Healthy soil = Healthy plants = Healthy profits.






